Private capital secondaries
Secondaries funds can offer investors returns that are differentiated to other private market strategies. On a risk adjusted basis these returns are particularly attractive, as a consequence of a number of advantages that secondary investing brings compared to primary investing:
- Enhanced diversification
- Acquisition of portfolios at a discount to NAV
- Shorter investment duration
- Reduction of blind pool risk
Secondaries past performance vs. other strategies
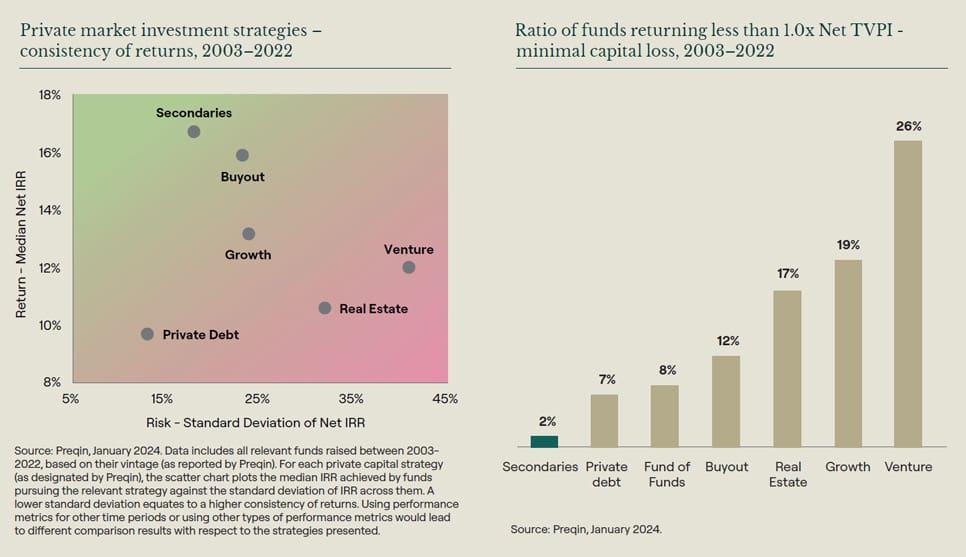
Investors have acknowledged the benefits of secondaries investments in providing exposure to private assets across economic and market cycles. Consequently, commitments to secondaries funds have grown consistently over the past decade.
Analysis using data from research company Preqin supports this conclusion. It shows an attractive risk-return profile for secondaries funds compared with other private market strategies.
Besides, compared to other private capital strategies, secondaries funds typically have a strong track record of capital preservation. The chart below shows the proportion of private capital funds with a net multiple below 1.0x by strategy, using data from research company Preqin.
Benefits of investing in secondaries
Buying at a discount to NAV
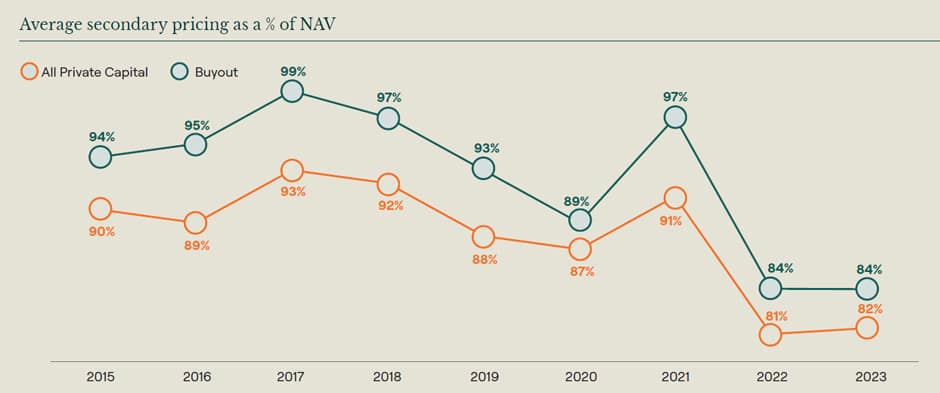
An advantage of investing in secondaries is the ability to acquire LP portfolios at a discount to their intrinsic value, something primary funds cannot do. The size of the discount achieved is based on the imbalance of supply and demand, which increases when liquidity is scarce, and the inefficiency of the market.
The graph below shows average secondary pricing for buyout portfolios and all private capital. In 2022 discounts widened, and buyout portfolios traded on average at 84% of NAV. This continued into H1 2023, which was characterized by a marked divergence in valuation expectations between buyers and sellers. As the year progressed, public market valuations improved, and valuation expectations started to converge. As a result, the year saw a modest increase in pricing for all private capital to 82%.
However, pricing of underlying transactions can vary significantly. Typically, there is stronger demand for ‘blue-chip’ GPs and younger vintage portfolios.
Diversification
Large secondaries funds typically have exposure to hundreds of underlying funds and thousands of portfolio companies, which can provide investors with diversification by investment strategy, geography, industry sector, and fund manager.
Moreover, secondaries funds offer the additional advantage of diversification by vintage year. This ability to back-fill a portfolio with ranges of historic vintages can be particularly valuable to investors either new to the private asset class or which have experienced a period of time where they were not investing.
Shorter investment duration
Because secondaries funds purchase interests at a later stage, the time to receive distributions is shorter. This means that their secondaries investors are expected to de-risk their exposure faster than primary investors and will have their cash at risk for a significantly shorter amount of time.
Reduction in blind pool risk
Secondaries investments are made in portfolios already substantially invested so buyers can conduct extensive due diligence on underlying assets and actively construct their portfolios. Therefore, the blind pool risks associated with primary fund investing are significantly reduced for secondaries investors.